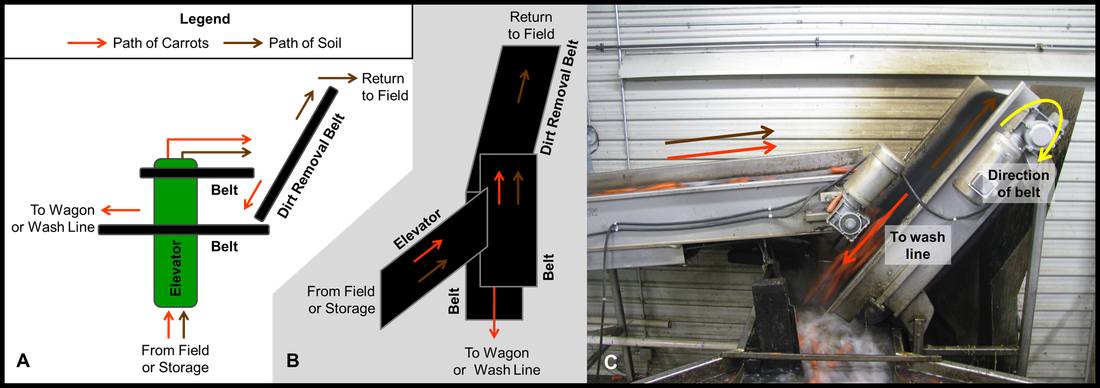
| Goal: Decrease the amount of soil entering a washwater treatment system. Solution: Install a dry soil removal system prior to vegetables entering the washing process. The vegetables are sent over a finger table (Figure 1) that jostles dried soil off. This system is also able to be used in the field on a harvester. Then they travel on a belt towards an angled belt where the vegetables roll down due to gravity and the angled belt, travelling in the opposite direction to the vegetables, carries soil or dried leaves away (Figure 2). The majority of the soil is removed by the finger table. |
Conclusion: The addition of a dry soil removal system diminishes the pressure on solids removal treatments and nutrient removal prior to discharge. They can be installed into an existing wash line with minimal modifications as they also act as conveyors or turning mechanisms.
Next Steps: The implementation of this type of system would have a great impact based on the collected data. If all the carrots grown in the Holland Marsh area including surrounding growing vicinities, an average of 44.6 kg of phosphorus would be prevented from entering the watershed.

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
