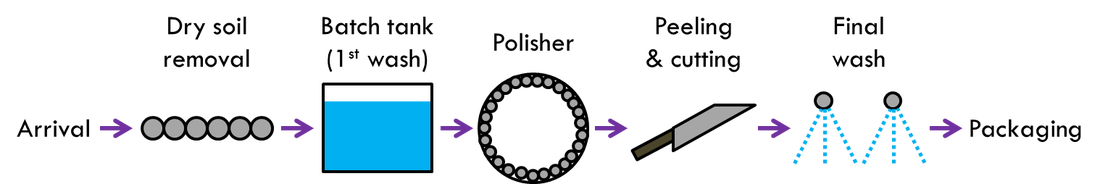
The first task to be completed is removing soil from the vegetables prior to a wet wash. A soil removal belt can jostle dried soil from the vegetable and reduce the amount of soil that will need to be subsequently washed and treated. The initial wash is usually done in a batch tank where the vegetables are dumped into water. This can also double as a flume to move them to the next step in the process. The water discharged from this step will require the most amount of treatment as it will have the highest concentration of soil.
Following initial washing, a polisher is used to do a final clean on the vegetables. This is done with a combination of water, brushes, and rollers to polish the roots. The last of the soil will be removed at this point. Nutrients and organic compounds from the vegetative material will also enter the water discharge stream due to the polishing.
In some facilities the vegetables will be peeled and cut. The water used in this process will have nutrients and organic (soluble) compounds when discharged.
The last stage before packaging is a final wash with potable water. This is required for food safety and the water discharged will carry little waste as the produce has been thoroughly cleaned in the previous steps. This water can also be re-used.
The amount of solids and nutrients in discharge water will depend on several factors. If a dry soil removal step is not present, all the soil will need to be washed off into the water, increasing the amount of solids in the discharge. There are also opportunities to reuse water from later stages in the preliminary steps; for example, the discharged water from a final wash can be used in the polisher and afterwards be added to the batch tank. In this way water is used more than once and a higher concentrated lower volume discharge is entering a treatment system.
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
