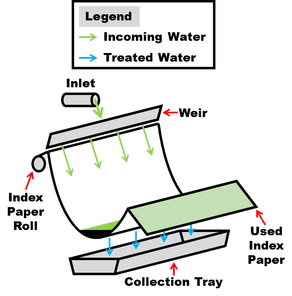
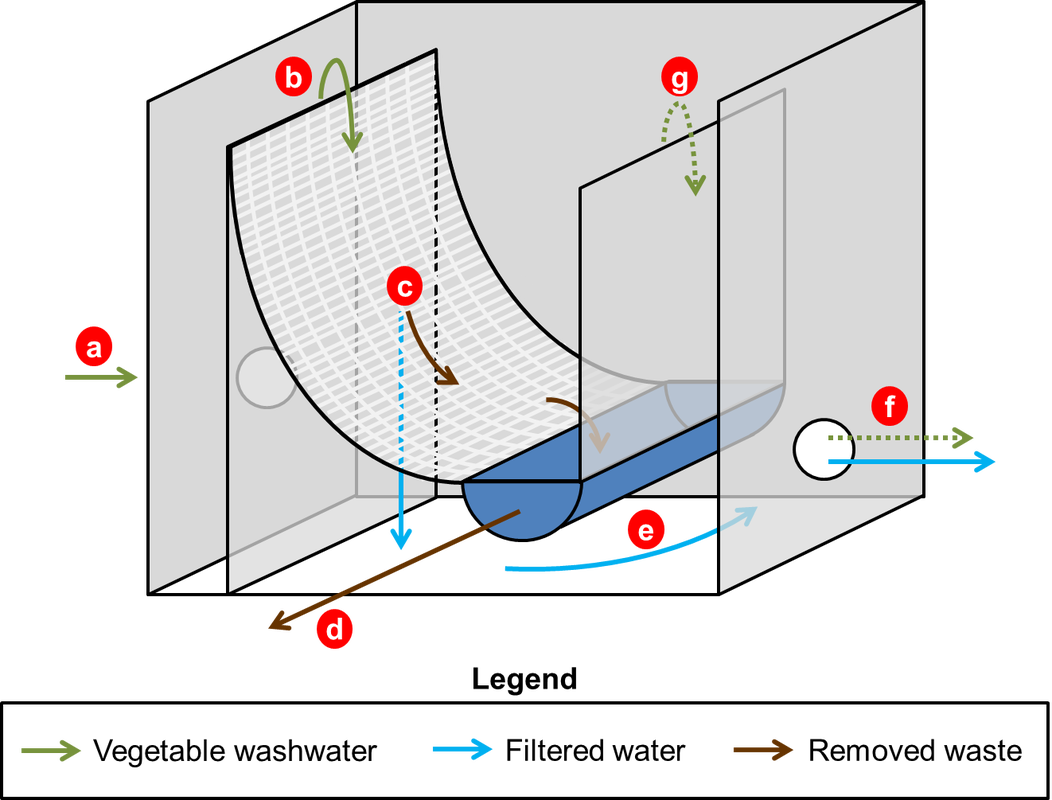
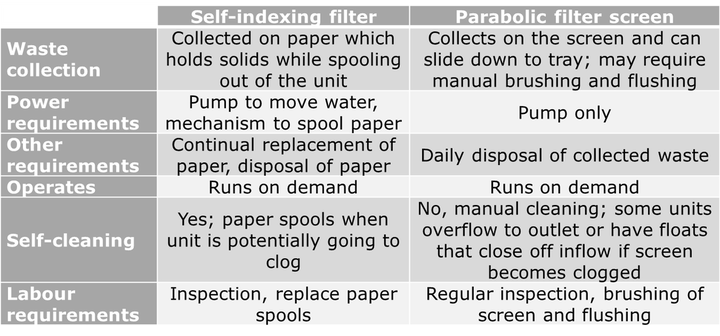
Solution: The operator looked at two different technologies, a self-indexing filter and a parabolic filter screen (Figures 1 & 2). Both are recommended units that filter coarse material from water.
Lesson Learned: When there are multiple technologies that could fit in a treatment system it is important to investigate all aspects. Decisions should be made based on more factors than merely cost.
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
